Key Takeaways
- What is pest management? Pest management combines prevention and targeted pest control methods to protect homes from infestations.
- Why is integrated pest management important? It reduces risks by using multiple safe and effective strategies instead of relying only on chemicals.
- How do you prevent household pests? Seal entry points, store food properly, control moisture, and maintain a clean environment.
- When should pesticides be used? Only as a last resort, with safety precautions to protect family, pets, and the environment.
- What’s the key to long-term pest control? Regular monitoring, seasonal maintenance, and adapting strategies to prevent recurring infestations.

“Pest Control: Do It Yourself vs …” from pestzone.net and used with no modifications.
Dealing with pests is an inevitable part of home ownership, but effective pest management doesn’t have to be complicated or toxic. With the right knowledge and approach, you can protect your home from unwanted invaders while minimizing risks to your family, pets, and environment. Effective pest management strategies focus on prevention first, followed by targeted intervention when necessary.
1. Pest Problems That Threaten Your Home and Health
Every region has its share of pests that can compromise your home’s structure, contaminate food sources, and potentially transmit diseases. Understanding what you’re up against is the first step in developing an effective defense strategy.
Common Household Pests and Their Dangers
Cockroaches carry bacteria that can trigger asthma and allergies while contaminating food preparation surfaces. These resilient insects have been linked to salmonella, E. coli, and other pathogens that cause serious illness. Their ability to survive in almost any environment makes them particularly challenging to eliminate once established.
Rodents like mice and rats cause extensive property damage by gnawing through electrical wiring, insulation, and structural components. A single mouse can contaminate far more food than it actually consumes, leaving behind urine, droppings, and hair that may contain harmful pathogens. These pests reproduce rapidly, with a single female mouse producing up to 10 litters per year. For more information on effective pest control methods, you can explore the integrated pest management approach.
Termites silently destroy wooden structures, often going undetected until significant damage has occurred. Unlike most pests that create nuisances or health hazards, termites directly attack your home’s integrity, potentially causing thousands in structural damage before they’re discovered.
Annual Pest Impact Statistics
$5 billion: Annual property damage from termites in the U.S.
21 million: American homes invaded by rodents each winter
82%: Percentage of homes with detectable cockroach allergens
$1,500-$7,500: Average termite treatment and repair costs
How Pests Damage Property and Spread Disease
Beyond the obvious property damage, pests create multiple health hazards in homes. Rodents contaminate surfaces with urine that remains invisible to the naked eye but contains pathogens that can survive for weeks. Cockroaches produce allergen proteins in their saliva, feces, and shed body parts that trigger asthma attacks, especially in children. Even seemingly harmless ants can contaminate food and create unsanitary conditions in kitchens and pantries.
Signs of an Infestation You Shouldn’t Ignore
- Droppings or urine stains, especially in cabinets or along walls
- Gnawed holes in food packaging or structural materials
- Unusual scratching sounds in walls or ceilings, particularly at night
- Discarded insect wings or shed skins
- Unexplained smells (musty odors from rodents or sweet, oily smells from certain insects)
- Visible tracks or grease marks along baseboards and walls
- Damaged wood with sawdust-like material (frass) near foundations
Early detection dramatically improves your chances of resolving pest problems before they become entrenched. Most homeowners miss early warning signs, allowing small problems to develop into full-blown infestations that require more aggressive treatment. Regular inspections of vulnerable areas like basements, attics, and food storage spaces can catch problems when they’re still manageable.
If you’re planning to relocate, consider hiring one of the best moving companies to ensure a pest-free transition.
When multiple signs appear simultaneously, you’re likely dealing with an established infestation rather than an isolated incident. The longer pests remain, the more difficult and expensive elimination becomes, creating a cycle that’s challenging to break without professional intervention.
2. Know Your Enemy: Identifying Pests Correctly
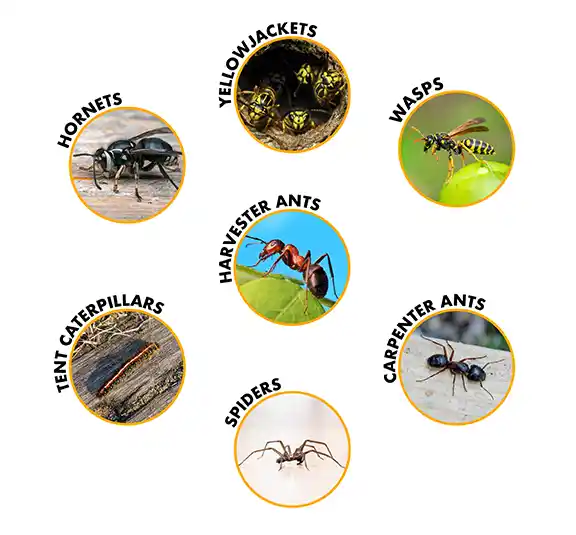

“How To Identify Common Pest Around Your …” from www.spectracide.com and used with no modifications.
Effective pest management begins with accurate identification. Applying the wrong treatment not only wastes time and money but can actually make certain pest problems worse. Many homeowners misidentify pests and use inappropriate control methods as a result.
Essential Tools for Pest Identification
A quality magnifying glass allows you to examine insects and their damage patterns in detail, revealing distinguishing characteristics that aren’t visible to the naked eye. Digital cameras or smartphone cameras with macro capability can capture images for later reference or to share with professionals for identification assistance. Online resources like university extension websites provide region-specific identification guides with photos and detailed descriptions of common pests in your area.
Consider creating a pest journal to document when and where you spot potential problems. This creates a valuable record that can reveal patterns and help identify seasonal pest pressures specific to your property. Many pest problems follow predictable cycles that, once understood, become much easier to anticipate and prevent.
Seasonal Pest Patterns to Watch For
Pests follow predictable seasonal patterns that smart homeowners can anticipate. Spring brings emerging ant colonies and termite swarms as temperatures rise, while summer heat drives cockroaches and flies to peak activity. Fall introduces rodents seeking winter shelter, with mice and rats becoming particularly aggressive about finding entry points. Winter dormancy for many insects doesn’t mean complete safety – this is when stored product pests like pantry moths and grain beetles often thrive in undisturbed food supplies.
Mistaken Identity: Pests That Look Similar
Carpenter ants and termites are frequently confused, yet require completely different treatment approaches. While both damage wood, carpenter ants excavate rather than consume it, leaving behind distinctive smooth galleries and sawdust-like waste. Termites actually digest wood fiber, creating mud tubes and leaving damaged wood that appears layered.
Bed bugs and carpet beetles represent another common case of mistaken identity. Both leave itchy welts on skin, but carpet beetles primarily damage fabrics rather than feeding on blood. Proper identification through careful inspection of specimens and damage patterns saves significant time and expense in treatment.
For those dealing with infestations, finding the best moving companies can also be a helpful step in ensuring that pests are not transported to a new location.
3. Prevention: Your First Line of Defense
Prevention represents the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to pest management. By eliminating the conditions pests need to survive – food, water, and shelter – you can dramatically reduce the likelihood of infestations before they begin.
Sealing Entry Points Around Your Home
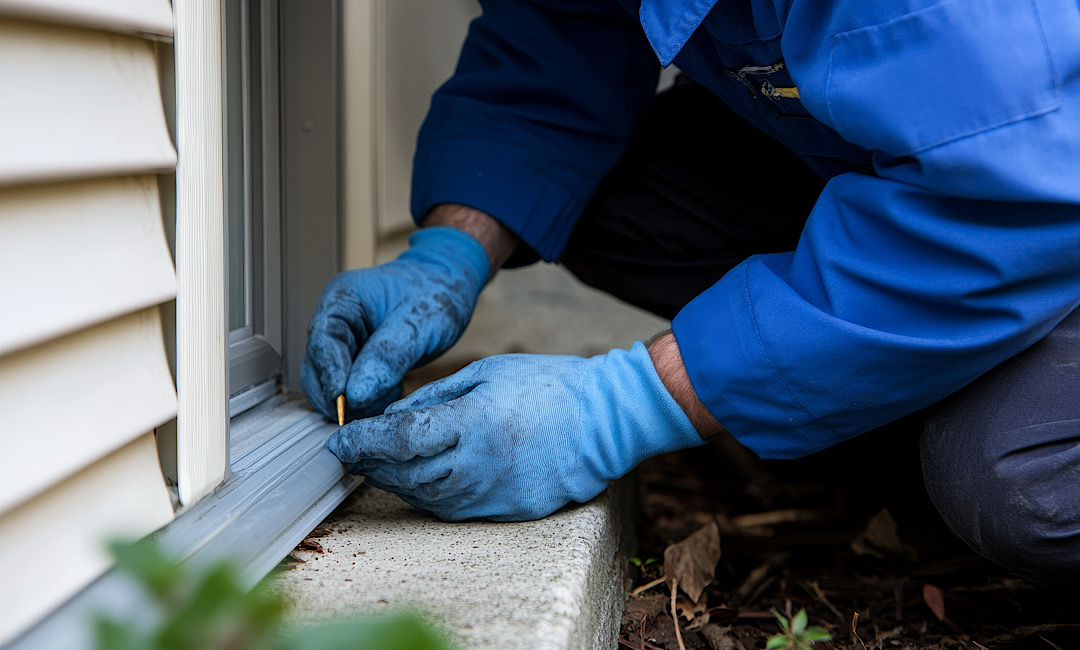

“Sealing Entry Points to Keep Pests Out …” from www.animal-pestcontrol.com and used with no modifications.
Most household pests enter through surprisingly small openings. Mice can squeeze through gaps as narrow as a pencil (¼ inch), while cockroaches need only a 1/16 inch space. Conduct a thorough inspection of your home’s exterior, paying special attention to areas where utilities enter, foundation cracks, loose siding, and gaps around doors and windows. Use appropriate materials for permanent sealing – steel wool embedded in caulk works well for larger openings, while silicone sealant addresses smaller cracks.
Weather-stripping exterior doors and installing door sweeps eliminates common entry routes while improving energy efficiency. Window screens should be inspected regularly for tears and repaired promptly. Remember that sealing must be comprehensive – pests will find the one opening you overlooked.
Smart Food Storage and Waste Management

“Glass Meal Prep Containers …” from www.amazon.com and used with no modifications.
Proper food storage eliminates the primary attraction for most household pests. Transfer dry goods like flour, sugar, cereals, and pet food from original packaging into sealed glass or hard plastic containers. This simple step removes access to food and eliminates hiding places within folded paper or cardboard packaging that many pests find ideal for nesting.
For additional tips on maintaining an organized home, check out the best moving companies for efficient packing and storage solutions.
Waste management practices significantly impact pest pressure. Use trash cans with tight-fitting lids both inside and outside your home. Empty indoor garbage frequently, especially food waste that attracts fruit flies and other insects. Compost bins should be positioned away from structures and designed to prevent rodent entry while still allowing proper decomposition.
Moisture Control and Landscaping Tips
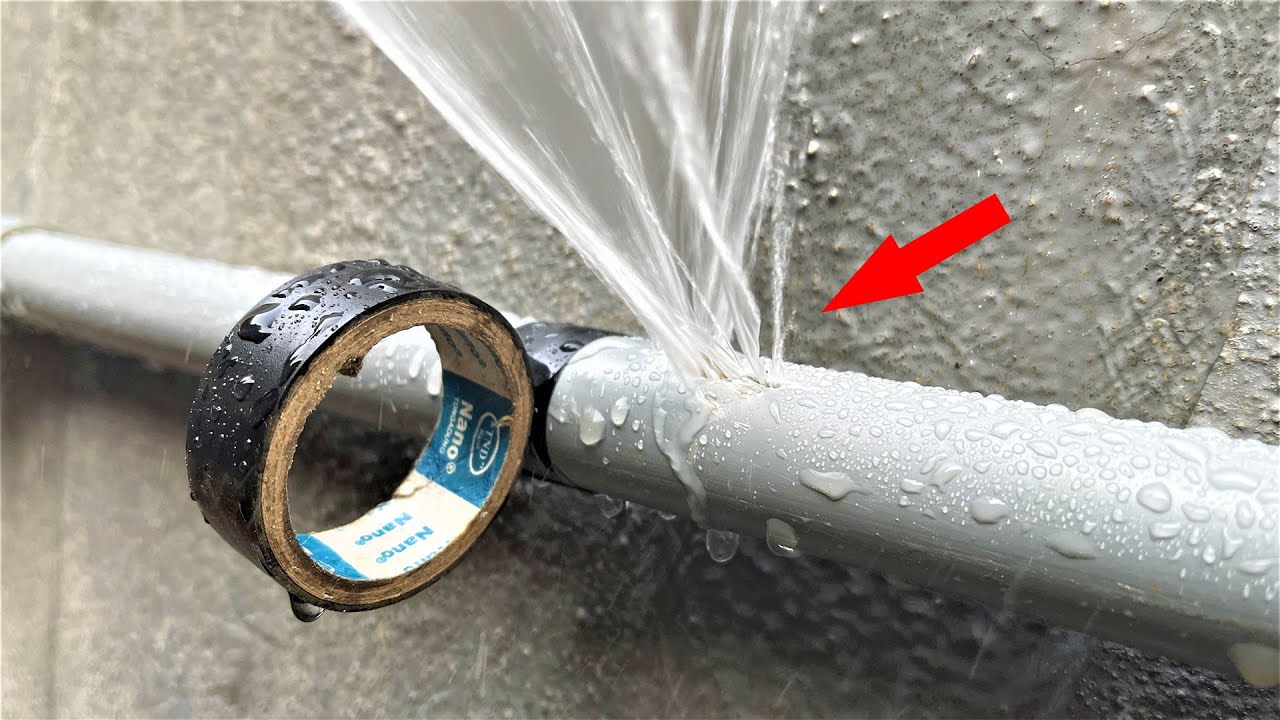

“Tips To Fix Broken Pvc Pipes Without …” from www.youtube.com and used with no modifications.
Water is essential for pest survival, making moisture management a critical prevention strategy. Repair leaking pipes promptly, address basement humidity with proper ventilation or dehumidifiers, and ensure gutters direct water away from foundations. Even small sources like pet water bowls or condensation under refrigerators can sustain pest populations when food is scarce.
Landscape choices influence pest pressure on buildings. Maintain a vegetation-free perimeter at least 18 inches from foundation walls to reduce humidity and eliminate hiding places. Trim branches that touch or overhang roofs, which create highways for rodents, ants, and other pests. Wood mulch retains moisture that attracts termites and provides shelter for numerous insects – consider using gravel or rubber mulch alternatives near foundations.
Regular Cleaning Habits That Deter Pests
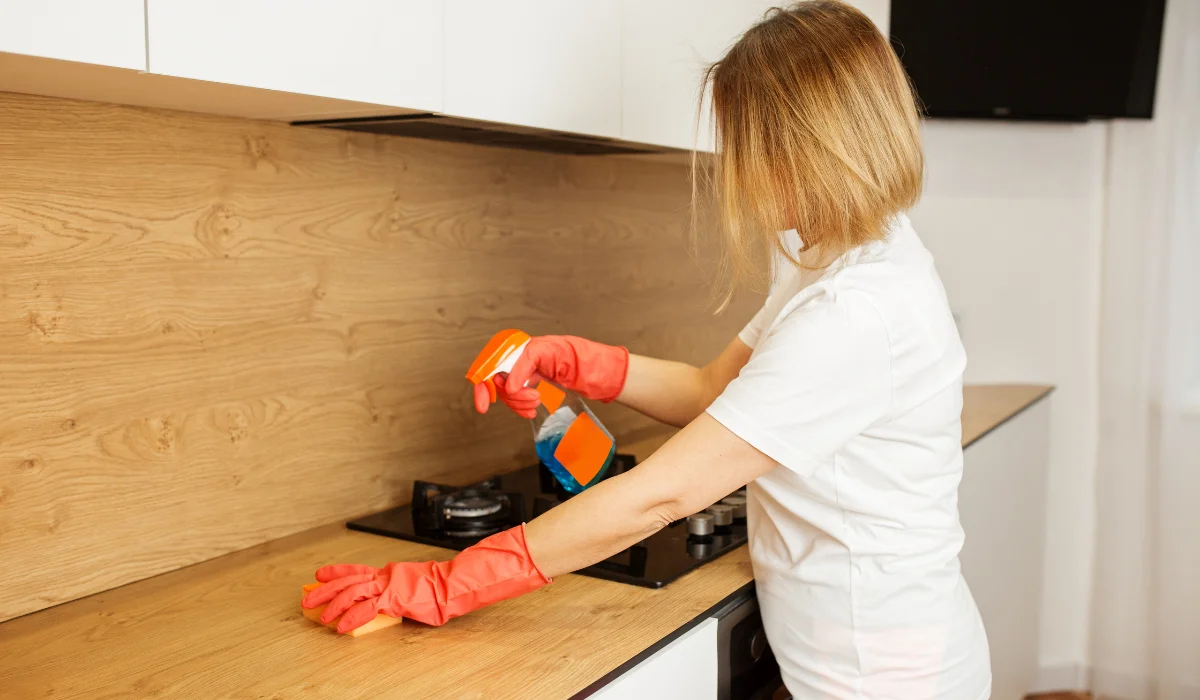

“Pest Control Clean-Up: How Long Should …” from www.lajaunies.com and used with no modifications.
Consistent cleaning disrupts pest establishment by removing food sources and destroying developing harborage areas. Focus on often-overlooked areas like under appliances, inside cabinets, and along baseboards where crumbs and debris accumulate. Vacuum thoroughly rather than sweeping, which captures more debris and can remove insect eggs before they hatch.
If you’re planning a move, consider hiring one of the best moving companies to ensure a clean transition and prevent pest issues in your new home.
Clutter elimination significantly reduces pest habitat. Cardboard boxes, newspapers, and rarely-used items create ideal nesting sites for rodents and hiding places for cockroaches. In garages and basements, store items in plastic containers off the floor to reduce harborage opportunities and make inspection easier.
4. Integrated Pest Management: The Smart Approach
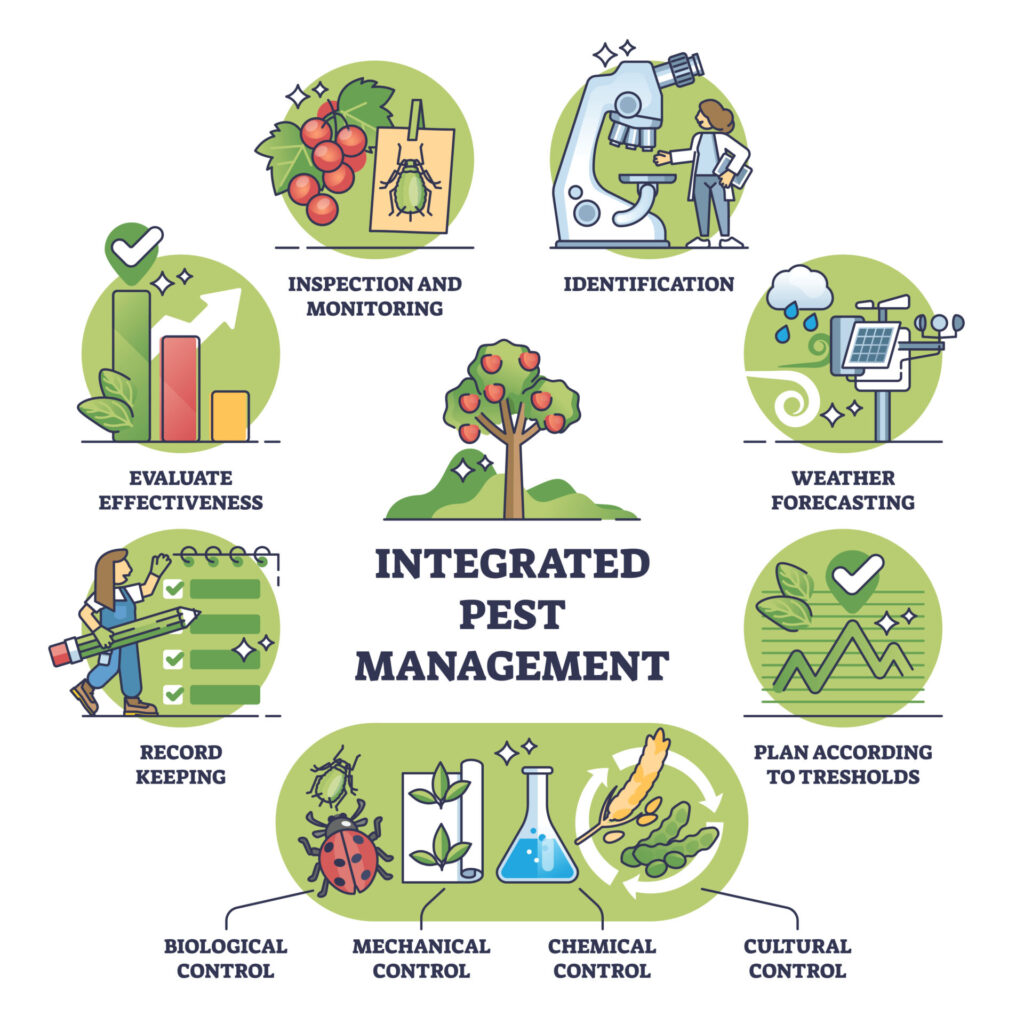
“What Is Integrated Pest Management?” from www.bizzybeeexterminators.com and used with no modifications.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) represents the gold standard for effective, sustainable pest control. This science-based approach combines multiple strategies to manage pest problems with minimal environmental impact. Rather than reacting to pest sightings with immediate chemical application, IPM follows a systematic process of prevention, monitoring, and targeted intervention only when necessary.
The IPM Hierarchy of Controls
1. Cultural/Sanitation: Changing behaviors that attract pests
2. Physical/Mechanical: Traps, barriers, and exclusion techniques
3. Biological: Introducing natural predators or parasites
4. Chemical: Least-toxic options applied precisely where needed
5. Conventional Pesticides: Used as last resort, specifically targeted.
Setting Action Thresholds Before Treatment
Action thresholds determine when pest control measures become necessary. Not every pest sighting requires intervention – a single ant exploring your kitchen doesn’t represent the same threat as a continuous trail of foragers. Establish realistic thresholds based on pest type, location, and potential harm before implementing control measures. For health-threatening pests like bed bugs or disease-carrying rodents, thresholds remain appropriately low, while occasional harmless visitors might be tolerated at higher levels.
Combining Multiple Control Methods
Effective pest management rarely relies on a single approach. By combining complementary methods, you create a more resilient system that prevents pests from adapting to any single control technique. Physical controls like traps and barriers work alongside habitat modification and judicious use of least-toxic chemical options when necessary. This integrated approach addresses different life stages and behaviors simultaneously, dramatically improving control results while reducing chemical dependence.
Monitoring and Adapting Your Strategy
Effective pest management requires ongoing monitoring to evaluate success and detect new problems early. Regularly inspect vulnerable areas like kitchens, basements, and entry points using flashlights to check dark corners and crevices. Simple monitoring tools like sticky traps provide continuous surveillance, capturing insects that might otherwise go unnoticed while revealing the types and numbers of pests present.
When control methods don’t deliver expected results, be prepared to adjust your approach. Pests can develop resistance to certain treatments or find alternative pathways around barriers. Document what works and what doesn’t, modifying your strategy based on observed results rather than continuing ineffective practices.
5. Chemical Controls: When and How to Use Them Safely

“Chemical methods of pest control” from mb.com.ph and used with no modifications.
While prevention forms the foundation of effective pest management, situations arise when chemical intervention becomes necessary. The key is using these tools judiciously, safely, and as part of a comprehensive approach rather than as the default solution.
Understanding Pesticide Types and Formulations
Pesticides come in various formulations, each with specific applications and safety considerations. Baits combine attractants with active ingredients, working well for social insects like ants and cockroaches that share food. Dust formulations penetrate wall voids and other hard-to-reach areas, providing long-lasting residual control. Liquid sprays offer immediate knockdown of visible pests but require careful application to avoid unnecessary exposure.
Target-specific products minimize risks to non-target organisms. For example, cockroach baits in child-resistant stations pose minimal risk to humans while effectively controlling infestations. Always choose the least toxic product that will effectively address your specific pest problem.
Reading Labels and Following Instructions
Pesticide labels are legal documents containing crucial information about proper use, safety precautions, and environmental protections. The application rate specified on the label has been scientifically determined for maximum effectiveness with minimum risk – using more product doesn’t improve results and may create unnecessary hazards. Pay particular attention to the “Environmental Hazards” section, which outlines potential impacts on beneficial insects, water sources, and wildlife.
Never use outdoor products indoors or vice versa, as formulations differ significantly based on intended application sites. Indoor products typically break down more quickly and are designed for use in enclosed spaces, while outdoor formulations may have longer residual activity and different safety profiles.
For more information on safe pest control practices, visit the EPA’s guide on pest control dos and don’ts.
Personal Protective Equipment Essentials
Proper protection during pesticide application prevents unnecessary exposure and potential health effects. At minimum, wear chemical-resistant gloves to prevent skin absorption, which represents a major exposure route even for relatively low-toxicity products. Eye protection shields against splashes or drift that could cause irritation or more serious injury. For aerosols or dust applications, consider using a mask rated for chemical protection to avoid inhalation exposure.
Safe Storage and Disposal of Chemicals
Store pesticides in their original containers with labels intact, out of reach of children and pets, preferably in locked cabinets. Temperature extremes can degrade active ingredients, so avoid garages or sheds that experience freezing temperatures or excessive heat. Never transfer pesticides to food or beverage containers, which creates serious poisoning risks through mistaken identity.
Dispose of empty containers according to label instructions and local regulations. Many communities offer hazardous waste collection events for unused or outdated pesticides. Never pour leftover products down drains or toilets, as they can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic ecosystems.
For those planning a move, consider hiring the best moving companies to safely transport hazardous materials.
6. Non-Chemical Alternatives That Actually Work

“Non-Toxic Pest Control Methods” from absolutepest.co.uk and used with no modifications.
Effective pest management doesn’t always require chemical solutions. Many non-chemical approaches provide excellent control while minimizing environmental impact and exposure risks.
Biological Controls and Natural Predators

“Biological Pest Control Stock Photos …” from www.istockphoto.com and used with no modifications.
Beneficial insects and microorganisms can help maintain balance in your landscape by controlling pest populations naturally. Lady beetles and lacewings voraciously consume aphids and other soft-bodied insects that damage plants. Beneficial nematodes effectively control soil-dwelling pests like grubs and fungus gnats without harming earthworms or beneficial soil organisms. For indoor environments, consider products containing Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a naturally occurring bacterium that targets specific insect groups without affecting mammals or beneficial insects.
Physical Traps and Barriers

“8 Pack Ranch Fly Traps,Fly Trap Outdoor …” from www.amazon.com and used with no modifications.
Mechanical controls capture or exclude pests without chemicals. Snap traps remain highly effective for rodent control when properly placed along walls where mice travel. Sticky traps monitor and capture crawling insects, providing valuable information about infestation levels while reducing populations. For flying insects, UV light traps attract and capture flies, moths, and mosquitoes in commercial settings and can be adapted for home use.
Physical barriers prevent pest entry and movement. Window screens, door sweeps, and mesh coverings for vents block flying insects while still allowing airflow. Copper mesh stuffed into gaps around pipes resists rodent gnawing while preventing entry. These passive measures work continuously without requiring reapplication or monitoring.

“Billy-Bob® Multi-Catch Mouse Trap …” from www.gertens.com and used with no modifications.
Heat, Cold, and Other Environmental Controls

“Bed Bug Heat Treatments – Zircon Pest …” from zirconpestsolutions.com and used with no modifications.
Temperature extremes effectively eliminate certain pests without chemical residues. Professional heat treatments raise room temperatures to 135-145°F for several hours, killing all life stages of bed bugs including eggs. This approach penetrates cracks and crevices where insects hide, reaching areas chemicals might miss. At the other extreme, freezing CO₂ (dry ice) effectively controls stored product pests in bulk foods by rapidly dropping temperatures below survival thresholds.
Diatomaceous earth, a powder made from fossilized diatoms, mechanically damages insect exoskeletons, causing dehydration and death. This low-risk material works well in dry areas where insects travel, like behind appliances or along baseboards. Unlike chemical residues, it remains effective indefinitely as long as it stays dry.
7. When to Call the Professionals

“Why Professional Pest Control Services …” from mothernaturesinc.com and used with no modifications.
While many pest problems can be managed independently, certain situations warrant professional intervention. Recognizing these scenarios saves time, money, and frustration while ensuring effective resolution.
| DIY-Appropriate Situations | Professional Intervention Needed |
|---|---|
| Occasional ant trails | Structural termite infestations |
| Small number of fruit flies | Established bed bug populations |
| Single rodent sighting | Wildlife in attics or walls |
| Seasonal spider problems | Recurring infestations despite DIY efforts |
| Preventative maintenance | Suspected dangerous species (brown recluse, etc.) |
Signs Your DIY Approach Isn’t Working
Persistent or worsening pest activity despite multiple treatment attempts signals the need for professional help. When infestations spread to new areas or return quickly after apparent elimination, underlying issues likely require professional assessment. Multiple pest species appearing simultaneously often indicates broader environmental conditions favoring infestations, requiring comprehensive intervention beyond spot treatments.
Choosing a Licensed and Reputable Pest Control Service
Look for companies with proper licensing, insurance, and membership in professional organizations like the National Pest Management Association. Reputable providers offer detailed inspections before recommending treatments and clearly explain their integrated approach rather than pushing monthly spray services as the only option. Check online reviews and ask neighbors for recommendations, focusing on companies that emphasize inspection, prevention, and targeted treatments rather than calendar-based spraying.
Questions to Ask Before Hiring
- What specific pests have you identified and what evidence supports this identification?
- What treatment methods will you use and why are they appropriate for this situation?
- What safety precautions should we take before, during, and after treatment?
- What preventative measures do you recommend to avoid future problems?
- Do you offer a guarantee or warranty for the service, and what does it cover?
- Are follow-up inspections included, and how will you determine if the treatment was successful?
What to Expect During Professional Treatment
Professional pest management begins with thorough inspection to identify pest species, infestation sources, and contributing factors. Technicians should provide clear preparation instructions before treatment, which might include moving furniture, clearing specific areas, or securing pets. During service, providers should communicate what they’re doing and why, identifying problem areas and explaining treatment strategies. Afterward, you’ll receive recommendations for preventing future issues, along with any necessary safety precautions related to recent applications.
8. Special Considerations for Families and Pets
Vulnerable Population Exposure Risks
Children: Higher respiratory rates, hand-to-mouth behaviors, developing systems
Pets: Lower body weight, grooming behaviors, floor-level exposure
Elderly: Potentially compromised immune systems, respiratory sensitivity
Pregnant women: Potential developmental impacts during critical periods
Families with children, pets, or vulnerable individuals require specially tailored pest management approaches. The goal becomes balancing effective pest control with minimizing exposure risks to those most sensitive to potential side effects. This often means emphasizing prevention, exclusion, and low-risk interventions while reserving chemical options for serious situations where benefits clearly outweigh risks.
Timing treatments strategically reduces exposure risk. Schedule applications when the home will be vacant for several hours afterward, allowing proper drying and ventilation before family members return. Remove children’s toys, pet bowls, and personal items from treatment areas to prevent indirect exposure through contact with these objects later.
Consider establishing treatment zones that create buffer spaces between living areas and pest habitats. For example, focusing rodent control in garages, attics, and external bait stations reduces the need for control products in main living spaces while still addressing the problem effectively.
Always inform your pest management professional about household members with special health considerations. Many companies offer specialized “green” or reduced-risk service options designed specifically for sensitive environments like schools, healthcare facilities, and homes with vulnerable occupants.
Child-Safe Pest Management Practices
Children face unique risks from pest control products due to their developing systems, hand-to-mouth behaviors, and proportionally greater exposure relative to body size. Store all pest control products, including seemingly harmless options like sticky traps, in locked cabinets out of children’s reach. Use tamper-resistant bait stations for rodenticides or insect baits, ensuring the active ingredient remains contained while still accessible to target pests.
Teach children appropriate behavior around pest management tools. Even young children can understand simple rules like “don’t touch the little boxes in the corners” when explained properly. Involve older children in preventative activities like proper food storage and cleanliness to build lifelong habits that reduce pest problems.
Protecting Pets During Pest Control
Pets require special consideration during pest management activities due to their proximity to treated surfaces, grooming behaviors, and smaller body mass. Remove pet toys, bedding, and food bowls before applications, and keep pets away from treated areas until products have completely dried. For yard treatments, follow label instructions regarding how long to keep pets off treated surfaces – this waiting period is based on scientific assessment of how long residues remain potentially harmful.
Managing Allergies and Sensitivities
Some individuals experience heightened sensitivity to both pests and the products used to control them. Cockroach allergens rank among the most common asthma triggers, making effective control essential for sensitive individuals, yet these same people may react to conventional pesticides. Focus on removing allergen reservoirs through thorough cleaning with HEPA vacuum cleaners and damp wiping of surfaces to remove accumulated pest debris and allergen particles.
When chemical sensitivity is a concern, explore heat treatments, freezing methods, or diatomaceous earth applications that control pests without introducing additional reactive compounds. Ventilation during and after any treatment helps reduce airborne concentrations of both pest allergens and control products, decreasing overall exposure.
9. Take Action: Your Seasonal Pest Management Plan
Effective pest management follows seasonal rhythms, anticipating and preventing problems before they develop. By understanding pest life cycles and behavior patterns throughout the year, you can implement preventative measures at optimal times, reducing the need for reactive treatments.
Creating a personalized calendar of inspection and maintenance activities transforms pest control from crisis management to routine prevention. This proactive approach identifies and addresses minor issues before they develop into major infestations, saving both money and stress in the long run.
Adapt your plan to your specific location and pest pressures. Coastal areas face different challenges than mountain regions, while urban environments present unique pest issues compared to rural settings. Local extension offices can provide region-specific information about pest timing and prevention strategies tailored to your area.
Annual Pest Management Calendar
January-February: Seal entry points during dormant period
March-April: Remove yard debris that harbored overwintering pests
May-June: Monitor for emerging ant colonies and termite swarms
July-August: Inspect for mosquito breeding sites, control moisture
September-October: Prepare for winter invaders seeking shelter
November-December: Focus on pantry pest prevention during storage season
Spring Cleaning and Inspection Checklist
Spring represents a critical time for pest prevention as many species become active after winter dormancy. Conduct a thorough exterior inspection as temperatures rise, checking for winter damage that might create entry points. Remove leaf litter, debris, and mulch built up against foundations that may harbor overwintering insects preparing to move indoors. Clean gutters and downspouts to prevent moisture accumulation that attracts pests and provides breeding sites for mosquitoes as temperatures rise.
Summer Vigilance Against Active Pests
Summer brings peak activity for many pest species, requiring increased monitoring and maintenance. Inspect door and window screens for damage that might allow flying insects entry, repairing tears promptly to maintain protection. Manage outdoor cooking and eating areas by promptly cleaning spills and storing food properly to prevent attracting ants, yellowjackets, and other opportunistic feeders.
For those planning a move during this busy season, consider hiring the best moving companies to ensure a smooth transition without pest-related disruptions.
Watch for signs of moisture-loving pests like cockroaches and silverfish, addressing humidity issues through proper ventilation, dehumidifiers, or air conditioning maintenance. Summer rains can drive certain pests indoors, so be particularly vigilant during wet periods when creatures seek shelter in dry structures.
Fall Prevention Before Winter Invaders Arrive
Fall preparations focus on denying shelter to pests seeking winter protection. Seal cracks and gaps in the building exterior, particularly around utility entrances and foundation perimeters, before cooling temperatures drive rodents indoors. Remove fallen fruit from landscape trees which attract yellowjackets, flies, and rodents when left to decompose on the ground.
Store firewood at least 20 feet from structures and elevated from the ground to prevent it from harboring rodents, carpenter ants, and termites that might eventually move indoors. Reduce exterior lighting that attracts flying insects, or switch to yellow “bug light” bulbs that are less attractive to nocturnal insects seeking winter harborage.
If you’re planning a move, consider researching the best moving companies to ensure a smooth transition while keeping pest management in mind.
Winter Maintenance to Prevent Indoor Issues
Indoor prevention becomes priority during winter months when households spend more time inside and pests concentrate in heated structures. Regularly inspect food storage areas, particularly products stored long-term like holiday baking ingredients, for signs of pantry pests. Maintain proper humidity levels to discourage moisture-dependent pests like cockroaches and silverfish while still preventing the dry conditions that promote static electricity and dry skin.
For more comprehensive pest management strategies, consider exploring integrated pest management practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns homeowners have about implementing effective pest management strategies. Understanding these fundamentals helps develop confidence in your approach and realistic expectations about results.
Remember that integrated pest management represents a process rather than a one-time event. Successful pest control combines multiple strategies adapted to your specific situation and implemented consistently over time.
How long does it typically take to eliminate a pest problem?
Timeline expectations vary significantly depending on pest species, infestation severity, and control methods employed. Simple problems like seasonal ants might resolve within days using proper baiting techniques, while established German cockroach infestations typically require 2-4 weeks of consistent management. Bed bug elimination often takes multiple treatments over 3-6 weeks to address all life stages, particularly eggs that resist many treatment methods.
Patience and persistence matter more than immediate results. Quick knockdown of visible pests may feel satisfying but often fails to address underlying populations. Sustainable control comes from methodical approaches that break reproductive cycles while eliminating conditions that supported the infestation initially.
Are natural pest control methods as effective as chemical ones?
Natural methods can be highly effective when properly matched to the pest problem and underlying causes. Diatomaceous earth provides excellent control of crawling insects in dry environments, while beneficial nematodes effectively target soil-dwelling pests like grubs and fungus gnats. The key is selecting appropriate methods based on pest biology and behavior rather than assuming all “natural” options work universally.
Integration often provides superior results to either approach alone. For example, combining sanitation, exclusion, and targeted application of botanical insecticides creates a more comprehensive solution than relying solely on either prevention or treatment. Success depends more on understanding pest vulnerabilities than on whether the control method is synthetic or natural in origin.
How can I prevent pests without endangering my children or pets?
Focus first on non-chemical strategies that create inhospitable environments for pests. Meticulous sanitation eliminates food sources, while physical exclusion prevents entry through weather-stripping, door sweeps, and screen repairs. Moisture management through proper ventilation, dehumidification, and prompt repair of leaks removes the water all pests require for survival without introducing any potentially harmful substances.
When interventions become necessary, consider contained approaches that minimize exposure. Tamper-resistant bait stations place active ingredients where only target pests can access them while protecting curious children and pets. Gel baits applied in small amounts to cracks and crevices provide effective control while remaining inaccessible to family members when properly placed.
What’s the difference between preventive pest control and reactive treatment?
Preventive control focuses on creating conditions that discourage pest establishment before problems develop. This proactive approach addresses structural vulnerabilities, sanitation practices, landscape management, and other factors that influence pest pressure. Regular inspections identify and correct minor issues before they develop into infestations, maintaining a continuously protected environment.
Reactive treatment responds to established problems after pests have already gained a foothold. While sometimes necessary, this approach typically requires more intensive interventions, often with higher environmental impact and cost. Most effective pest management programs combine strong prevention with targeted reaction when necessary, gradually shifting toward prevention as control improves.
How often should I schedule professional pest inspections for my home?
Most homes benefit from annual professional inspections to identify developing issues before they become serious problems. These assessments should include both interior and exterior examinations, with particular attention to vulnerable areas like crawl spaces, attics, and utility entrances. Properties with historical pest pressure or specific risk factors may require semi-annual inspections to maintain protection.
The best inspection schedule considers your specific situation, including home age, construction type, location, and previous pest history. Professional assessment provides trained eyes that spot subtle signs homeowners might miss, like frass from wood-boring insects or early warning signals of moisture problems that could attract pests.
Pest management is crucial for maintaining a healthy and safe environment, whether it’s in residential areas or commercial spaces. Effective pest control strategies not only prevent property damage but also safeguard health by minimizing the spread of diseases carried by pests. Understanding the various methods and approaches to pest control can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions. For those seeking professional assistance, it’s important to choose a service that uses environmentally friendly methods and offers comprehensive solutions.
Additionally, staying informed about the latest advancements in pest management can provide a competitive edge, much like how quantum computing is changing business landscapes.

